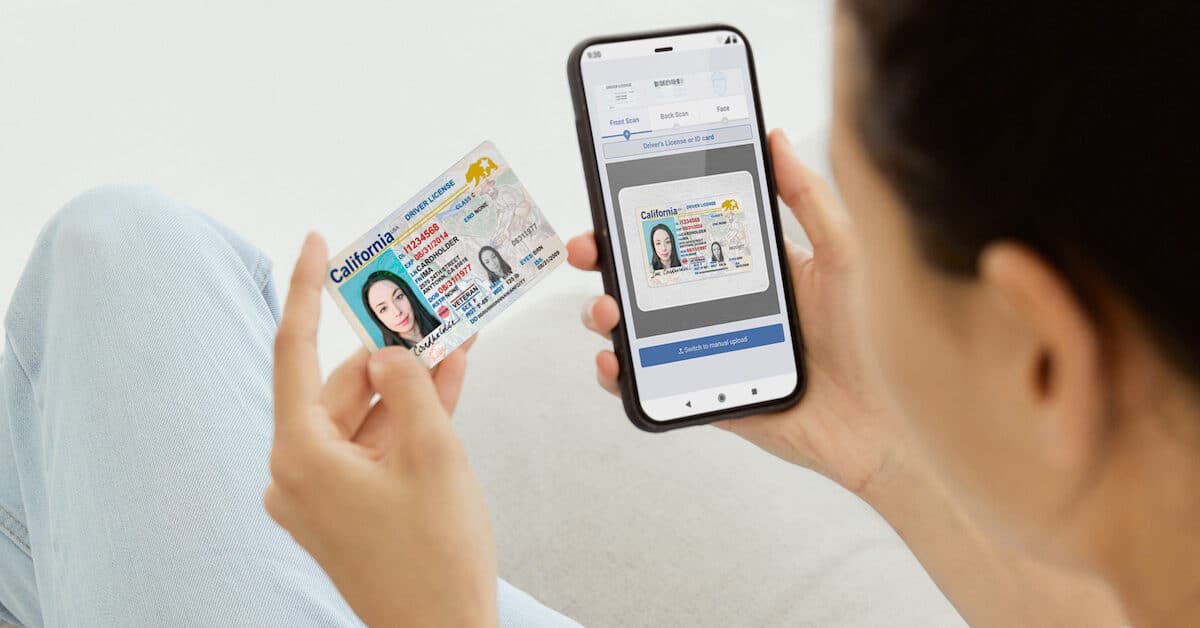
According to McKinsey & Co, organizations plan to grow digital interactions by more than 50% by 2024. This means increased emphasis on seamless digital onboarding and account creation, as well as enhanced check-out, reservation, and customer inquiry processes. Today’s consumer wants to onboard as quickly and seamlessly as possible.
In the age of digital platforms, it can be tricky to conduct proper identity verification while maintaining a streamlined customer experience. Usernames and passwords are simply no longer enough identity verification to stand up to today’s cybercriminals. And they don’t meet KYC or AML standards which are increasingly being applied across a broad range of business types.
Confidence in your digital identity verification processes is paramount in ensuring your company’s digital security, so let’s take a look at a few of the identity verification methods available and evaluate possible pros and cons.
Knowledge-based authentication (KBA)
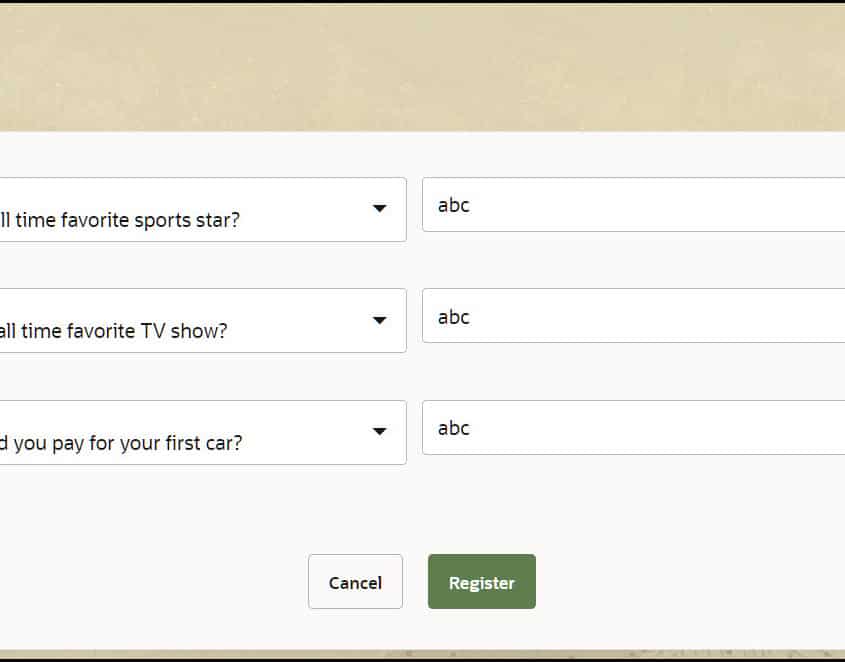
You have probably used knowledge-based authentication before as it’s one of the most common forms of identity verification.
KBA uses security questions (also known as “challenge questions”) for identity validation, designed to be easy for the user to answer, but difficult for a stranger to guess. Some common examples being, What is your mother’s maiden name? or Which of the following addresses have you been associated with? KBA questions are generated by querying various public record sources including credit report agencies, cellphone providers, rideshare services, and more.
As an additional level of security, timers can be employed to ensure that the answer isn’t being researched by either a person or a computer program. This is a decent method of identity verification since most users are familiar with it, but unfortunately, the security questions’ answers can often be easily guessed using social media or manipulated out of the customer through social engineering. Social engineering is the act of manipulating someone into divulging personal information about themselves for identity verification, usually via email or text message.
Pros of knowledge-based authentication
- High level of customer familiarity means low levels of abandonment
- Inexpensive to implement due to long history, commoditization
- Hard for fraudsters to use at scale
Cons of knowledge-based authentication
- Social engineering, such as online quizzes, or social media phishing, can get users to reveal answers to KBA questions, allowing fraudsters to impersonate them later.
- Users often cannot remember the answers to obscure questions such as childhood addresses, or old services used in the past.
Two-factor authentication (2FA)
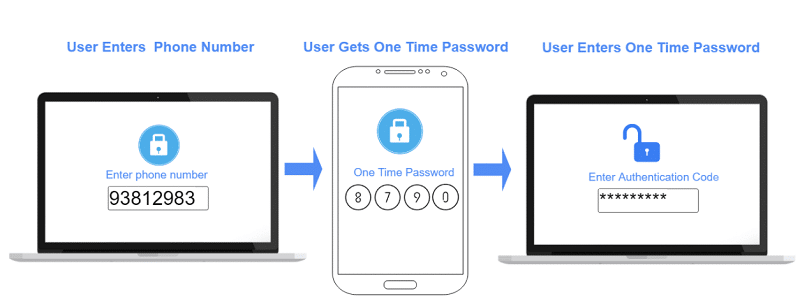
Two-factor authentication is another method of identity verification that has become de rigeur. NIST protocols now demand multi-factor authentication as a basic layer of security for any business that does business with the US government.
As the name suggests, it includes authentication from two sources for identity verification. The first method is typically a username and password, but the second factor is a random string of number and/or letters that can be sent to the users email address or cell phone number. The code is usually time sensitive and expires after a certain period of time. As with KBA, 2FA is a well-known identity verification method and is usually quite simple to perform as most people have their cell phone nearby to receive authentication codes. However, if this code is given to anyone else or if social engineering is employed to steal the code, this method of identity verification can also be somewhat easily compromised. 2FA is also reliant on the user’s cell and/or internet service so, in some cases, the third party could slow the identity verification process.
Pros of 2FA
- Real-time. 2FA ensures that the user has access to at least 2 identity sources simultaneously, making it difficult for fraudsters to fake.
- 2FA apps make it easy for customers to manage 2FA from a single portal, managed by their phone password or biometric login.
Cons of 2FA
- Two factor authentication requires that the customer have access to their phone and/or email address at the time of account creation. The process of getting the 2FA code from the secondary source can lead to abandonment if the second factor is not readily accessible.
Credit bureau-based solutions
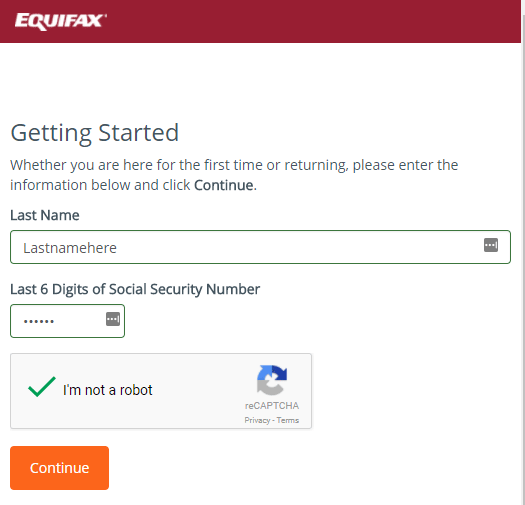
This form of identity verification relies on information from major credit bureaus such as Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion to provide identity verification information about potential customers, such as name and social security number. Using large credit bureaus to verify that your customer is who they say they are is fast, cost-effective, and easy to implement, but it also comes with some downsides.
The credit bureaus are subject to cybersecurity breaches, e.g., the massive Equifax data breach in 2017, and these data breaches have given cyber-criminals access to personal, extremely sensitive information. This method of identity verification can also be tricky for those who haven’t built up credit yet, such as young people or individuals new to the country, or those who just haven’t used mainstream financial services. Due to the aforementioned reasons, customers like these aren’t easily found within the credit bureaus’ databases and are basically excluded from using this identity verification method.
Pros of credit bureau based identity verification
- Data is typically very reliable
- Credit score and credit worthiness can provide a rich picture of the risk profile of a particular consumer, which has value beyond just verifying their identity.
- Credit-bureau based reporting is typically KYC compliant due to the stringent requirements that credit bureaus are under.
Cons of credit bureau based identity verification
- Many users get nervous when they see names like Equifax of Experian because they are worried they are going to trigger a hard credit-pull. This can increase abandonment and customer-service calls
Device or account-based verification

Device or account-based identity verification solutions use online, offline, and social media data for identity validation or to detect if someone committing fraud. They use many different sources for identity verification and provide a confidence score based on how likely it is that fraud is being committed. However, database identity verification solutions are easily spoofed by creating fake social media profiles and online identities. They are also often not KYC (Know Your Customer) or AML (Anti-Money Laundering) compliant, so they might need to be used in conjunction with other identity verification solutions to ensure identity validation.
Pros of device or account verification
- Most people have relatively stable patterns of usage for items such as their mobile phone or social media account. Therefore these common logins can typically be trusted.
- Applications such as Google and Facebook offer OAuth logins, so users can create accounts utilizing platforms where they have already been verified.
Cons of device or account-based verification
- It is relatively easy for fraudsters to create fake social media profiles or email accounts in another person’s name.
- If a user has recently changed devices, or opened a new account, they will likely be flagged as fraudulent, even if they are a legitimate customer.
ID verification-based solutions
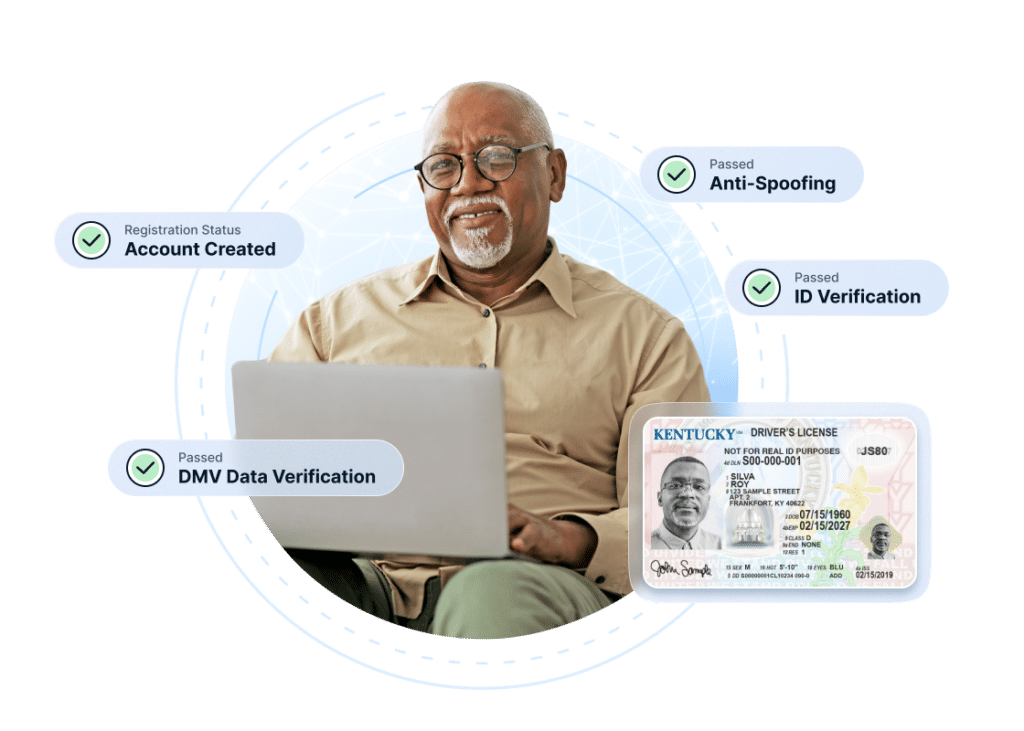
Online identity verification is often a great cybersecurity solution as it also provides identity validation by examining the customer’s ID and comparing it to a selfie the customer takes. This face matching process quickly and efficiently compares the ID image to the selfie by creating a mesh model of the face to check for accuracy and liveness. This anti-spoofing technology is beneficial because it helps to prevent against things like deep fakes and other fraudulent attempts.
The technology automatically performs identity verification by checking that the ID is formatted correctly based on individual state guidelines. It also checks that the information in the barcode matches what is displayed on the front of the ID. The identity verification platform then confirms the accuracy of the address listed by checking it against know databases. The final, and arguably most important step in this process is the face matching process. After creation of the mesh model, the AI technology compares multiple points on the face and head to compare similarity and liveness(meaning you can’t just upload a picture of the person that you got offline. It has to be a specific type of picture).
While this might seem like a long, drawn out process just to confirm identity, 99% of the work is being done by AI in only 1 minute, sometimes less. Once the comparison is complete, the Digital Identity Verification will give you a confidence score based on how likely it is that the ID and selfie both match and are not fraudulent.
In addition to the above checks, the Digital Identity Verification (DIVE API) platform that IDScan.net offers, various third party checks can be layered into the process to add even more insight into the person needing to be verified. One common example is a DMV integration. driver’s licenses or other state issued ID cards have long since been used as proof of identity, so this DMV integration allows the user to check the data on a specific ID against the information stored in the DMV database to ensure the information is accurate.
Overview of the features of different types of digital identity verification
A quick overview of the different features you’ll find with various digital identity verification options
| Type of digital identity verification | ID-based | Credit Bureau Based | 2-Factor Authentication | Knowledge Based |
| Requires access to identity document | ✓ | |||
| Requires recall of historical data | ✓ | |||
| Requires SSN | ✓ | Possibly | ||
| Requires access to secondary account (email/phone) | ✓ | |||
| Requires customer history | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| Performs face-matching | ✓ | |||
| Checks human identity in real-time | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Protects against spoofing | ✓ | |||
| At risk due to social engineering | ✓ | ✓ |
What are the methods of digital identity verification?
There are several commonly used methods for verifying identity online:
- Two factor authentication
- Credit-based authentication which performs a soft-pull from credit bureaus
- Document/selfie based verification (known as IDV)
- Knowledge-based authentication
There are many out there for digital identity verification, but only a couple that truly ensure accuracy and validity. Be sure to contact our team to learn more about how our Digital Identity Verification solution can be quickly and easily integrated into your pre-existing website or app





