Last updated on August 21st, 2024 at 01:06 pm
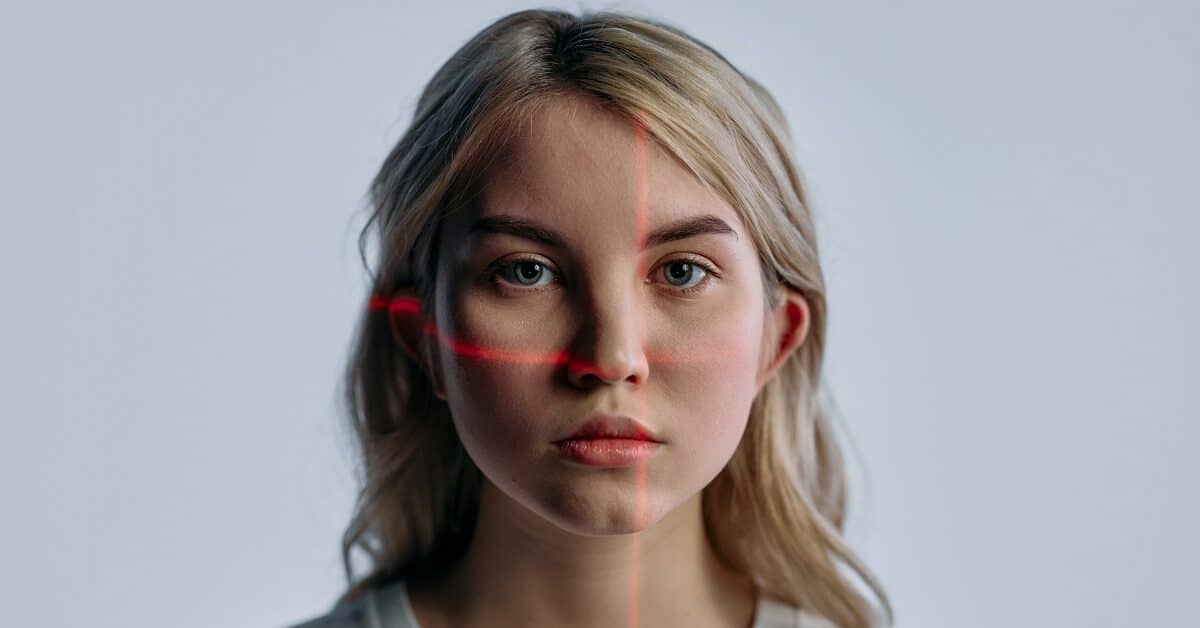
Biometrics are the use of physical or behavioral characteristics to identify individuals. In the context of identity verification, biometric authentication systems use unique biological or behavioral features of a person to verify their identity.
Biometric features may include facial recognition, fingerprints, iris or retina scans, voice recognition, hand geometry, or even behavioral traits such as typing patterns or walking gait. These features are captured by sensors and then compared with the pre-existing biometric data stored in a database to confirm or deny the identity of the person.
Biometric authentication systems are becoming increasingly popular in areas such as banking, security, and mobile devices. They are considered to be more secure than traditional methods of identification, such as passwords or personal identification numbers (PINs), as biometric features are much harder to forge or steal.
Facial recognition
This technology uses cameras to capture an image of a person’s face, which is then compared to a database of stored images to verify their identity. The system analyzes key facial features, such as the shape of the face, distances between eyes, nose, and mouth, and unique landmarks. It extracts numerical representations (face templates or face embeddings) that capture these distinctive features. The extracted face templates or embeddings are compared against a database of known faces or enrolled templates. This comparison is typically done using mathematical algorithms that calculate the similarity between the templates.
Strengths of facial recognition for biometric identity verification
Non-invasive
Relatively inexpensive due to its maturity in the market
Works quickly and accurately.
Can be used in real-time and in one-to-many scenarios, or as face matching in one-to-one scenarios
Weaknesses of facial recognition for biometric identity verification
Commonly cited as a privacy concern due to its ability to be used without consumer knowledge using mounted cameras
Can be impacted by lighting and changes in appearance (glasses, facial hair, etc.)
It’s important to note that there are different approaches to facial recognition, such as 2D-based methods that analyze images or videos, and 3D-based methods that use depth information to create a more accurate representation of the face.
Fingerprint recognition
Fingerprint recognition, also known as fingerprint biometrics, is a technology that identifies and verifies individuals based on their unique patterns of ridges and valleys on their fingertips. The first automated fingerprint identification system (AFIS) was introduced in the 1960s. It utilized early computer technology to digitize and store fingerprint data for efficient matching and retrieval. These early AFIS systems were primarily used by law enforcement agencies to aid in criminal investigations.
Strengths of fingerprint recognition for biometric identity verification
High level of accuracy as fingerprints do not change over time
Wide acceptance due to use by law enforcement and in consumer technology
Small hardware footprint
Low privacy concerns since physical proximity is required to collect a fingerprint
Weaknesses of fingerprint recognition for biometric identity verification
Fingerprints can be difficult to capture in wet or dirty conditions
Requires physical access to the individual and cannot reliably be used in remote identity verification scenarios
Fingerprint recognition systems can use various algorithms, such as ridge-based matching, correlation-based matching, or minutiae-based matching. Machine learning techniques, such as neural networks, can be employed to train the algorithms and improve the accuracy of fingerprint recognition. Fingerprint biometrics has gained widespread adoption and acceptance across various industries, including law enforcement, access control, financial institutions, and mobile devices. It has proven to be a reliable and efficient method of identification due to the uniqueness and permanence of fingerprints.
Iris recognition
Iris recognition is a biometric technology that identifies individuals based on the unique patterns of their iris, which is the colored part of the eye surrounding the pupil. An iris recognition system captures a high-resolution image of the individual’s iris using specialized cameras or sensors. The person is usually required to position their eye within a designated area for accurate image acquisition. The iris region is identified and isolated from the rest of the eye image through a process called iris localization and segmentation. Algorithms are used to detect the boundaries of the iris and exclude irrelevant information, such as eyelids and eyelashes.
Key features are extracted from the iris image to create a unique template or code. These features typically include characteristics such as the arrangement of crypts (furrows), ridges, and other intricate patterns present in the iris. Various algorithms, such as phase-based encoding or Gabor filters, are employed for feature extraction.
This unique pattern is then compared to a database of stored iris images to verify their identity.
Strengths of iris recognition for biometric identity verification
Patterns are highly distinctive and do not change over time, making iris recognition extremely accurate
Works well even in low-light environments.
Weaknesses of iris recognition for biometric identity verification
Requires cameras near the eye and direct eye contact with an individual and thus does not work in one-to-many matching scenarios
Requires physical access to the individual and cannot reliably be used in remote identity verification scenarios
Can be expensive to implement due to novel technology and specialized hardware
Privacy and security measures are critical when implementing iris recognition systems. Iris data is typically stored in encrypted form, and strict protocols are followed to ensure the protection and proper handling of individuals’ biometric information.
Iris recognition has found applications in various fields, including access control, border security, forensic investigations, and identity management.
Voice recognition
This technology uses software to analyze a person’s voice patterns, which are then compared to a database of stored voice patterns to verify their identity. Voice recognition technology captures and analyzes various vocal characteristics to create a unique voiceprint for each individual. These vocal characteristics include factors such as pitch, tone, cadence, accent, pronunciation, and even physical characteristics of the vocal tract. The voiceprint is created by extracting and storing specific features and patterns from an individual’s voice.
Strengths of voice recognition for biometric identity verification
Non-invasive
Can be used remotely
Can be used for both verification and identification
Weaknesses of voice recognition for biometric identity verification
Accuracy can be impacted by background noise or changes in the person’s voice
Can be impacted by health conditions that affect the person’s voice
Susceptible to deepfake fraud
Privacy measures play a crucial role in ensuring the secure and responsible use of voice recognition for biometric identity verification. Voice data is treated as sensitive personal information and protected using appropriate security measures. This includes encryption during storage and transmission, access controls, and secure storage practices to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
Voice recognition is commonly used in applications such as phone banking, call center authentication, voice-controlled devices, and access control systems.
Hand geometry
Hand geometry is a biometric modality that uses the physical characteristics of a person’s hand to verify their identity. Hand geometry recognition involves capturing and analyzing specific measurements and features of the hand to create a unique biometric template. Here’s some more information about hand geometry for biometric identity verification:
Strengths of hand geometry for biometric identity verification
Easy to use and non-invasive.
Can work in a variety of conditions and is widely used in security applications
Weaknesses of hand geometry for biometric identity verification
Can be impacted by changes in the person’s hand, such as injuries or aging
Can be difficult to capture accurately
Hand geometry data should be protected using appropriate security measures. This includes encryption during storage and transmission, access controls, and secure storage practices to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
Hand geometry recognition is commonly used in applications such as access control systems, time and attendance tracking, and physical security applications. It provides a reliable and user-friendly biometric solution for identity verification.
Signature recognition
Signature recognition, also known as signature verification, is a biometric technology that analyzes and verifies an individual’s signature for identity verification purposes. It involves capturing and analyzing various features and patterns present in a person’s signature to create a unique biometric template.
Strengths of signature recognition for biometric identity verification
Widely used and can be implemented easily in a variety of applications
Weaknesses of signature recognition for biometric identity verification
Can be impacted by changes in the person’s signature over time
Vulnerable to forgery
When implementing signature recognition systems, privacy measures should be implemented to protect the collected signature data. This includes obtaining clear consent, securely storing and transmitting the data, implementing access controls, and complying with relevant data protection regulations.
Signature recognition is commonly used in applications such as document authentication, financial transactions, and legal agreements. Its convenience and familiarity make it a popular choice for identity verification, especially in contexts where handwritten signatures are traditionally used.
Behavioral biometrics
Behavioral biometrics refers to the measurement and analysis of an individual’s behavioral patterns or traits for the purpose of identity verification. Unlike physical biometrics, which focus on anatomical or physiological characteristics, behavioral biometrics capture and analyze unique behavioral attributes exhibited by individuals during their interactions with systems or devices. Some examples include keystroke dynamics, mouse dynamics, and gesture recognition.
Strengths of behavioral biometrics for biometric identity verification
Can be used in combination with other biometric technologies for added security
Can be used in a variety of applications
Weaknesses of behavioral biometrics for biometric identity verification
Can be impacted by changes in the person’s behavior
May not be as accurate as other biometric technologies
Behavioral biometrics involve the collection and analysis of user behavior, raising privacy considerations. Organizations should implement appropriate measures to ensure data protection, informed consent, and compliance with relevant privacy regulations.
Behavioral biometrics are increasingly being used in various applications, such as user authentication, fraud detection, access control, and continuous monitoring. They offer an additional layer of security and user convenience, complementing other forms of biometric identification and authentication methods.
Conclusion
Overall, there are many different biometric technologies available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Organizations will need to choose the biometric technology that is best suited to their specific needs and use case.
IDScan.net has already implemented several forms of biometric identity verification into our software, but as technology advances, we will continue to add more security features. To learn more about how our biometric screening works, be sure to contact a member of our team or schedule a demo.