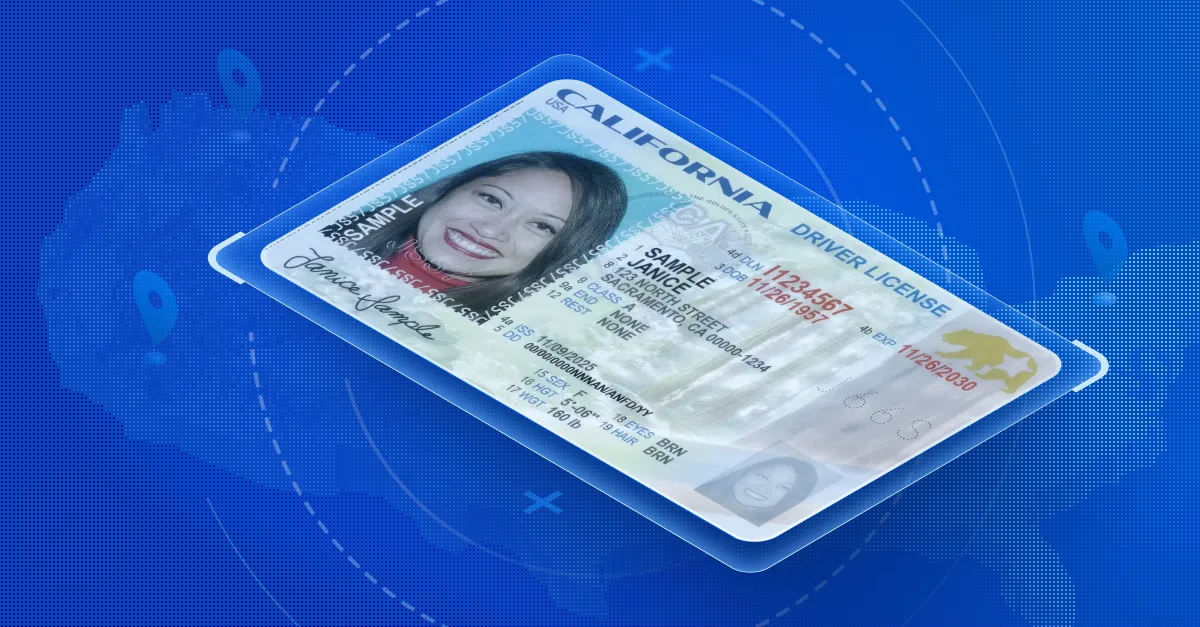
California issues some of the most widely used identity documents in the United States. With nearly 40 million residents, California drivers licenses and identification cards are presented daily across retail, hospitality, transportation, financial services, cannabis, and more. As ID formats evolve and fraud tactics become more sophisticated, understanding how California IDs are structured, and how to properly verify them, is critical for businesses that rely on accurate identity and age verification.
In recent years, the California Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) has introduced multiple updates to its physical credentials, including a newly redesigned driver’s license format and expanded support for mobile IDs. These changes improve document security but also introduce new challenges for organizations still relying on outdated verification technology.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of California IDs, including current license formats, security features, mobile ID developments, verification challenges, and how IDScan.net supports accurate age and identity verification across all California credential types.
Overview of California Identification Documents
The California DMV issues several types of government-issued identification credentials, including:
- California driver’s licenses
- California identification cards (non-driver IDs)
- REAL ID–compliant licenses and ID cards
- Commercial driver’s licenses (CDLs)
- Digital and mobile driver’s licenses
Each credential serves as legal proof of identity and, in many cases, age eligibility for restricted activities such as alcohol purchases, cannabis sales, gaming, and venue access.
California IDs are governed by federal REAL ID standards, AAMVA barcode requirements, and state-specific security mandates. As a result, the state routinely updates its card designs to maintain compliance and combat increasingly advanced counterfeit techniques.
California REAL ID program

California offers both REAL ID–compliant credentials and standard non-REAL ID licenses. REAL ID cards are marked with a gold bear and star symbol in the upper corner and are required for federally regulated activities such as boarding domestic flights or accessing secure federal facilities.
From a verification perspective, REAL ID and non-REAL ID California cards contain the same barcode data structure, but REAL ID credentials include additional document verification requirements during issuance, making them more trusted by third parties, but not immune to fraud.
California driver’s license format update
In late 2024 and into 2025, the California DMV began rolling out a redesigned driver’s license and identification card format. This update introduced both visual and technical changes intended to strengthen security and modernize the card layout.
The new design includes several key changes:
- Updated background artwork featuring California landmarks
- Modified typography and layout of demographic fields
- New placement of the ghost image and portrait
- Enhanced security printing techniques
- Removal of the traditional magnetic stripe
- Introduction of a digitally signed barcode
These changes were implemented to reduce counterfeiting, prevent barcode cloning, and align California credentials with emerging digital identity standards.
Security features found on California IDs
In addition to the visible security features and design elements, modern California driver’s licenses and ID cards also incorporate multiple layered security features designed to combat alteration and forgery.
Common security features on California IDs include:
- Laser-engraved text and images
- UV-reactive artwork visible under blacklight
- Microprinting embedded within background patterns
- Tactile text elements
- Ghost photo imagery
- Overlapping security artwork
- Digitally signed PDF417 barcode
The digitally signed barcode is one of the most significant updates, allowing verification platforms to authenticate whether barcode data has been altered or artificially generated.
California domiciled and non-domiciled commercial driver’s licenses (CDLs)
In addition to standard driver’s licenses and identification cards, the California Department of Motor Vehicles also issues commercial driver’s licenses (CDLs) for individuals authorized to operate commercial motor vehicles. California CDLs are governed by both state regulations and federal Department of Transportation (DOT) requirements, making accurate identity verification especially important for employers, logistics providers, and transportation operators.
The state has historically issued two primary CDL classifications: domiciled and non-domiciled commercial driver’s licenses.
California domiciled commercial driver’s licenses
A California domiciled CDL is issued to drivers who legally reside in the state of California. These license holders must provide proof of California residency during the application process and are subject to all standard state requirements, including REAL ID documentation standards when applicable.
Domiciled CDLs include the same foundational security features found on standard California driver’s licenses, such as laser engraving, microprinting, UV imagery, and digitally signed barcodes. However, they also contain additional commercial indicators, including license class designations, endorsement codes, and restriction fields that identify the type of commercial vehicles the individual is authorized to operate.
Because CDLs are frequently targeted for fraud and impersonation, automated scanning and authentication play a critical role in confirming both identity and license validity.
California non-domiciled commercial driver’s licenses
Historically, a non-domiciled CDL was issued to individuals who operate commercial vehicles in California but maintain legal residence in another country or jurisdiction. These licenses were commonly issued to foreign national drivers who meet federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) requirements but do not qualify as California residents.
However, as of September 29, 2025, the state has stopped issuing the license type after the Interim Final Ruling was released. With over 62,000 CDLs and 5,000 CLPs in California being non-domiciled, the ruling greatly impacted California transportation and logistics providers.
Non-domiciled CDLs differ from domiciled licenses in several important ways:
- They are typically not REAL ID–compliant
- They include visible “Non-Domiciled” identifiers
- Issuance requires additional federal eligibility documentation
- Validity periods may differ from standard CDLs
While the physical card layout remains similar to other California licenses, non-domiciled CDLs may contain distinct text indicators or coding within the barcode data that identify the holder’s residency status.
Verification challenges with the new California ID format
California is one of the first states to utilize the latest version of AAMVA’s guidance on barcode structure (including the additional security features). For this reason, some ID scanner apps and ID authentication tools may have trouble properly validating California IDs unless they have been updated to work with the new AAMVA standard.
Also, the new template has significant overlap between the colorful design, holographic security features, and text present on the front of the ID. If an ID scanning software solution relies on optical character recognition (OCR), there may be challenges in accurate parsing of the text on the front of the ID.
Additionally, the ID’s barcode contains a secret security signature, which is intended to keep fraudsters from easily spoofing the document. If your ID scanning software is not able to detect IDs which lack this barcode signature, you may have challenges reading new California IDs.
Rise of California mobile IDs
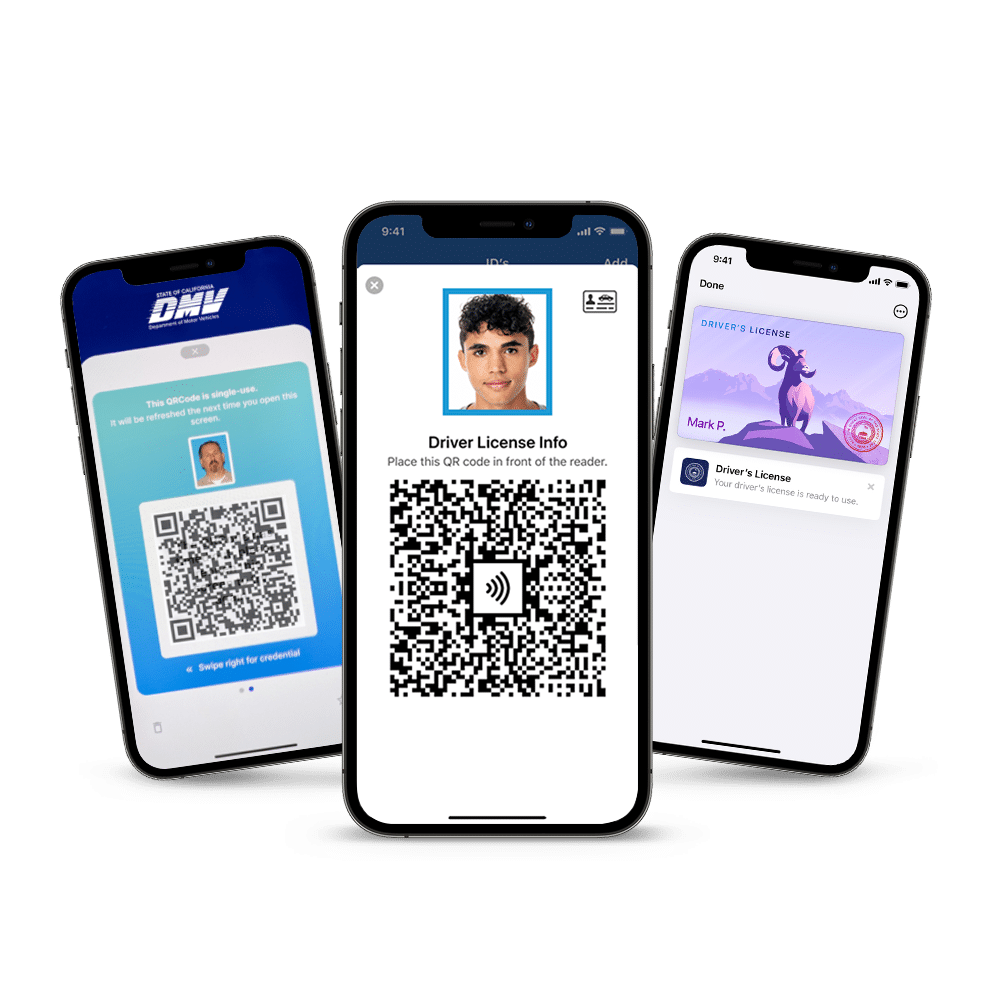
California has also expanded access to digital identity through mobile driver’s licenses stored in Apple Wallet, Google Wallet, and the California DMV Wallet app.
These California mobile IDs allow residents to present a secure digital credential in supported environments, such as TSA checkpoints and participating businesses. Mobile IDs use encrypted data transmission and user-controlled sharing to limit exposure of personal information.
For example, individuals may share age-only verification data without revealing their full date of birth or address.
As mobile IDs gain adoption, verification systems must be capable of validating both physical and digital credentials.
Why accurate California ID Verification Matters
Improper verification of California IDs can expose organizations to significant risk that lead to non-compliance, hefty fines, or in extreme situations, even jail time.
Manual visual inspection alone is no longer sufficient to detect sophisticated fake IDs, especially as counterfeiters replicate surface-level security features with increasing accuracy.
Automated ID verification is now considered a best practice across regulated industries.
How IDScan.net supports California ID verification
Identity verification solutions, like VeriScan and ParseLink are designed around modern regulatory and technical realities. If your use case is to automate an eligibility check (for discounts, sign-in, or age/identity restricted services) while minimizing legal risk, implementing one of the aforementioned solutions is an easy way to improve existing workflows. Combined with customizable smartflows, businesses can accept any legal form for California ID, be it physical or mobile.
- Accurately scan and verify various forms of identification, including passports, state IDs, and drivers licenses, international IDs, and mobile IDs ensuring compliance.
- Utilize adaptive AI and machine learning algorithms to detect fake or counterfeit IDs, adding an extra layer of security.
- Ensure that the solutions adhere to state and federal data privacy regulations, safeguarding customer information during the scanning process.
- Provide a detailed record that can be exported for legal purposes and used in risk mitigation.
- Integrate into existing workflows or establish new ones when the need arises. This seamless workflow enhances operational security without adding friction to the customer experience.
Selecting the appropriate ID scanner is also important when factoring in use cases and scanning restrictions. For barcode-only scans, a non-image capture ID scanner is the more appropriate choice. For businesses requiring authentication, a more advanced ID scanner would be recommended. This allows businesses to meet California age-verification requirements while reducing human error and liability.
Support for Mobile ID Verification
Residents in the Sacramento area can share their TruAge QR code at checkout at select retail locations. This companion app allows users the ability to pick and choose which bits of your personal information you share based on what is needed at your location. In the past, you just had to hand over your entire ID, but now Californians will select what information they want shown, and only the required information will be displayed to the individual scanning.
IDScan.net and Apple
IDScan.net has integrated the VeriScan for iOS application with Apple to allow for NFC capable mobile ID scanning. This is done much like the process for Apple Pay. Once initiated inside the VeriScan app, both devices are then held near each other, and data is securely shared from the Apple Wallet version of mobile IDs from participating states, including California. The data can also be shared via a QR code that is generated from the consumer’s phone. The encrypted and secure method helps streamline processes for businesses while ensuring the same standard of age verification used by traditional handheld scanners.
IDScan.net and Credence ID
IDScan.net has also partnered with Credence ID and their Tap2ID mobile ID reader. The Tap2ID reader is wired directly to a computer, where it sends the results of the “scan” of each mobile driver’s license verification into the VeriScan for Windows platform. Tap2iDTM accepts mobile driver’s licenses issued by more than 14 states including California, including the mDLs available through Apple, Samsung, and Google wallets. This new platform also accepts IDs presented using state-developed wallets or non-native applications. The Tap2ID mobile ID reader can act as a standalone solution if desired, but it can also be easily integrated into existing workstations and processes that businesses have in place.
Preparing for the future of California IDs
California remains at the forefront of identity modernization. With redesigned physical credentials, digitally signed barcodes, and mobile ID expansion, verification technology must evolve alongside state issuance programs.
Businesses that rely on outdated scanning tools risk verification failures, compliance gaps, and increased fraud exposure. Those using modern, adaptive platforms are better positioned to handle both current and future California ID formats.
Conclusion
California IDs are among the most complex and frequently presented identification documents in the country. As license formats evolve and digital credentials become more common, accurate verification requires more than a visual check.
IDScan.net provides trusted solutions for both age verification and identity verification of California IDs, supporting all variations of the state’s identity credentials.
By leveraging purpose-built verification technology, businesses can confidently accept California IDs while maintaining compliance, protecting customer data, and reducing risk.