Last updated on June 25th, 2025 at 02:47 pm
How are KYC and AML different and how do they work together?
KYC and AML are both necessary for many companies to comply with governmental regulations. These can be asked of banking institutions, casinos, financial management, and investment trading just to name a few. While they can work in tandem to accomplish similar goals, they are different concepts and require different levels of information.
What are KYC and AML?
KYC, which stands for Know Your Customer, is a process required to verify the identity of customers, and is a subset of AML regulations. KYC is commonly required in industries including banking, trading, blockchain, payments, telecom, and financial management to prevent money laundering and fraud. But KYC also has a wider scope of implementation than AML – KYC processes can help a range of businesses, even those in industries not legally mandated to implement.
AML stands for anti-money laundering. This is a process that prevents criminals from depositing or transferring money that comes from illegal activity such as terrorism and criminal financing. AML processes check for known fraudsters, terrorists, politically exposed persons, and more. This measure is specifically meant to target market manipulation, trade of illegal goods, corruption of funds, and tax evasion. AML checks are commonly required in banking, casinos, currency exchanges, payment and investment industries, real estate, and the insurance industry.
The goals of the two processes are different – KYC ensures businesses verify who each customer is, usually during onboarding, while AML is an ongoing process of monitoring transactions to ensure legality.
| Aspect | eKYC (Know Your Customer) | AML (Anti Money-Laundering) |
| What is it? | The process of digitally verifying a customer or user’s identity in order to safely transact or do business | A set of policies and procedures intended to prevent money laundering through financial institutions, casinos, and other business entities where money is exchanged |
| Scope | Focused exclusively on customer identity | Focused on checking confirmed customer identity against specific lists, and ongoing monitoring of behavior |
| Primary Objective | Confirm who a customer is, and assess risk | Detect and prevent illicit financial activities like money laundering or financing terrorism |
| Included Steps | – Document verification – Biometric authentication (typically via selfie) – Risk scoring | – Checks against AML/PEP/Sanctions lists – Ongoing monitoring for suspicious activity |
| Timing | Primarily during customer onboarding | Ongoing throughout the customer lifecycle |
| Regulatory Requirements | Required as part of AML laws. Recommended for many use cases to prevent fraud. | A legal compliance framework required under laws such as: – Bank Secrecy Act (1970) – USA Patriot Act (2001) – Anti-Money Laundering Act (2020) – AML Directive (EU) – Proceeds of Crime Act (UK) – Prevention of Money Laundering Act (India) Many more |
| Technology required | – Digital document verification – Biometric authentication (selfie face-match) – Logic tree and e KYC software | – Transaction monitoring software with alerting – Watchlist screening – Case management system |
| Risk focus | Individual customer fraud risk | Systemic financial crime and organized crime risk |
| Examples | Scanning a passport and asking for a selfie during the account creation process | Flagging a pattern of cash deposits that is outside the typical scope of an account |
How do KYC and AML interact?
AML and KYC processes are often confused, as KYC is a component of AML. KYC is the step in the process that ensures the customer is who they say they are. AML ensures not only this but also involves continuous monitoring of their transactions to ensure legal activity.
While AML is an umbrella term for the range of regulatory processes firms must have in place, KYC is a component of AML that consists of firms verifying their customers’ identity.
How can KYC be integrated into an existing platform?
Verifying and re-verifying identity is an integral part of KYC and maintaining cybersecurity, both in-person and online. Our remote ID validation system efficiently verifies identity, leaving your customers with a streamlined and headache-free experience on your site or app. It’s also easily integrated into current systems to avoid labor hours spent on backend integration and training.
To use our eKYC software, the customer simply can complete a series of checks on their smartphone.
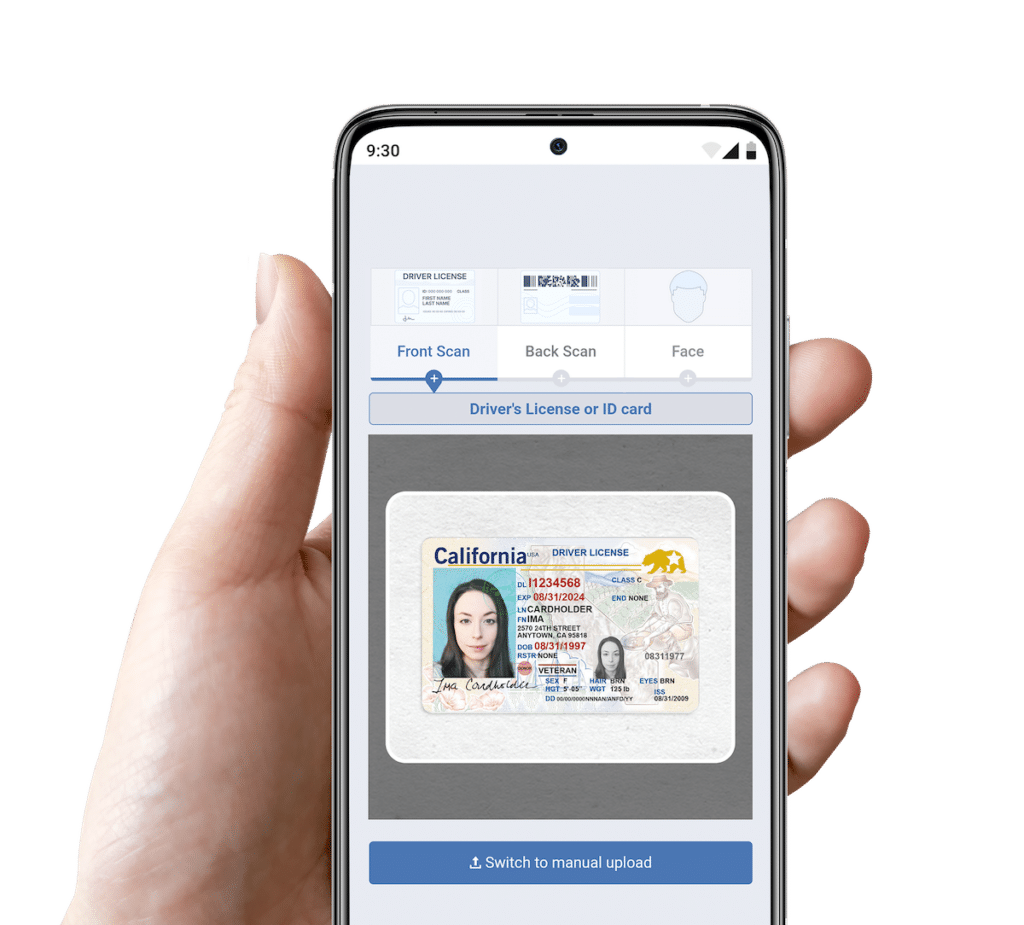
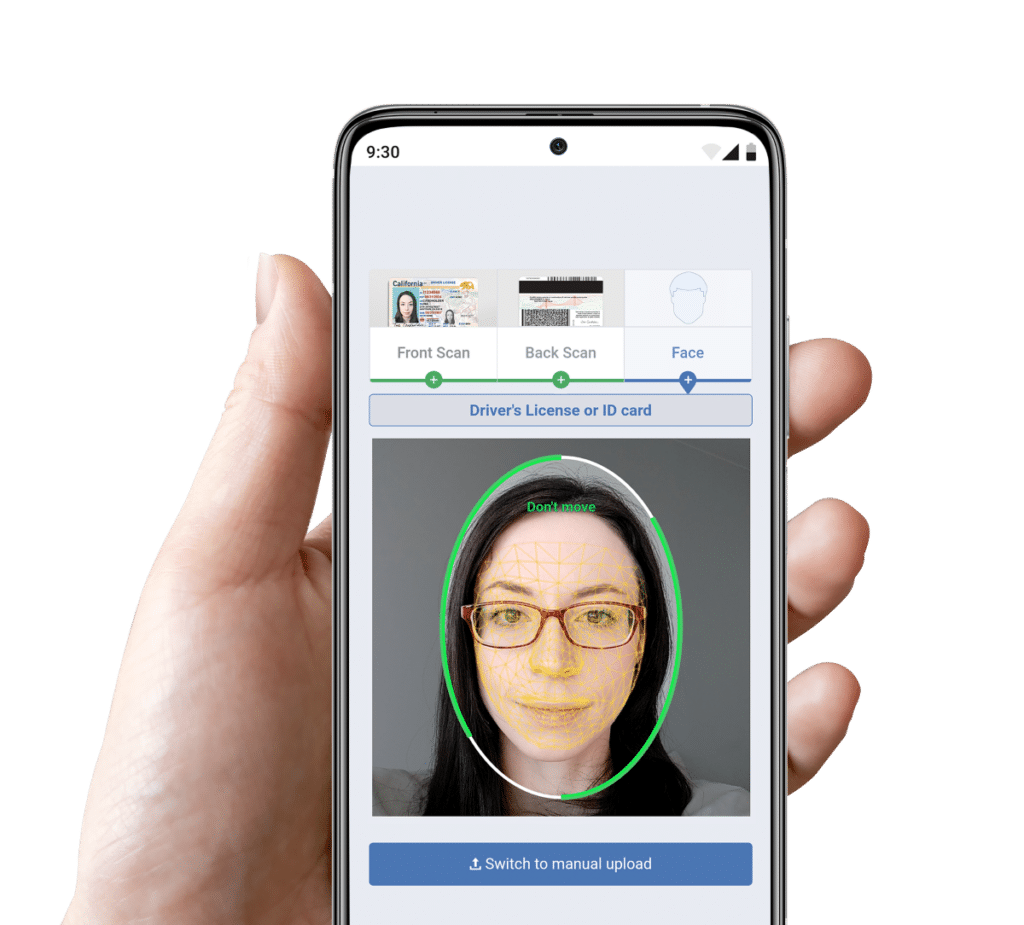

The automation performs mobile ID verification by checking that the ID is formatted correctly on the front and back. It also checks that the information in the barcode matches what is displayed on the front of the ID. It then queries the USPS database to confirm that the address on the ID exists. Lastly, it moves to the pictures, calculating a confidence percentage in facial match between the photo on the ID and the selfie supplied by the customer. The selfie is run through anti-spoofing processes to ensure it is legitimate.
The customer’s picture is first compared to a database of known faces to ensure that a human face is indeed pictured. A complex algorithm then maps the customer’s face and compares the unique layout of the pictured face to the face on the ID provided. The mobile ID verification automation can then see more definitively whether or not the faces match and provides a percentage to represent the confidence it has in the faces being the same. Additionally, our DIVE API can verify most identification documents including driver’s licenses, passports, passport cards, green cards, and international documents with an MRZ (Machine Readable Zone).